proxy_lab
本实验分为三个部分:设置代理、并发、缓存
准备部分:安装netstat工具
1 | sudo apt install net-tools |
1. 实现一个顺序的代理服务器
概述
- 在第一部分,设置代理来接受传入连接,读取和解析请求,转发请求到Web服务器,读取服务器的响应,并将这些响应转发给相应的客户端(用于处理HTTP/1.0的GET请求)
- 启动时,你的代理应该监听在命令行指定的端口上接收传入连接。一旦建立了连接,代理应该从客户端读取整个请求并解析请求。它应该确定客户端是否发送了有效的 HTTP 请求;如果是,则可以建立自己的连接到适当的 Web 服务器,然后请求客户端指定的对象。最后,代理应该读取服务器的响应并将其转发给客户端
代码实现
- 首先包含必须的库
1 |
- 做一些基本定义
1 | // 定义基本常量 |
- 实现核心处理函数
1 | void doit(int fd){ |
- 实现URI解析函数
1 | void parse_uri(char *uri, char *hostname, char *port, char *path){ |
- 实现HTTP请求头构造函数
1 | void build_reqheader(rio_t *rp, char *newreq, char *method, char *hostname, char *port, char *path){ |
- main函数实现监听
1 | int main(int argc, char** argv) |
检测
1 | make |
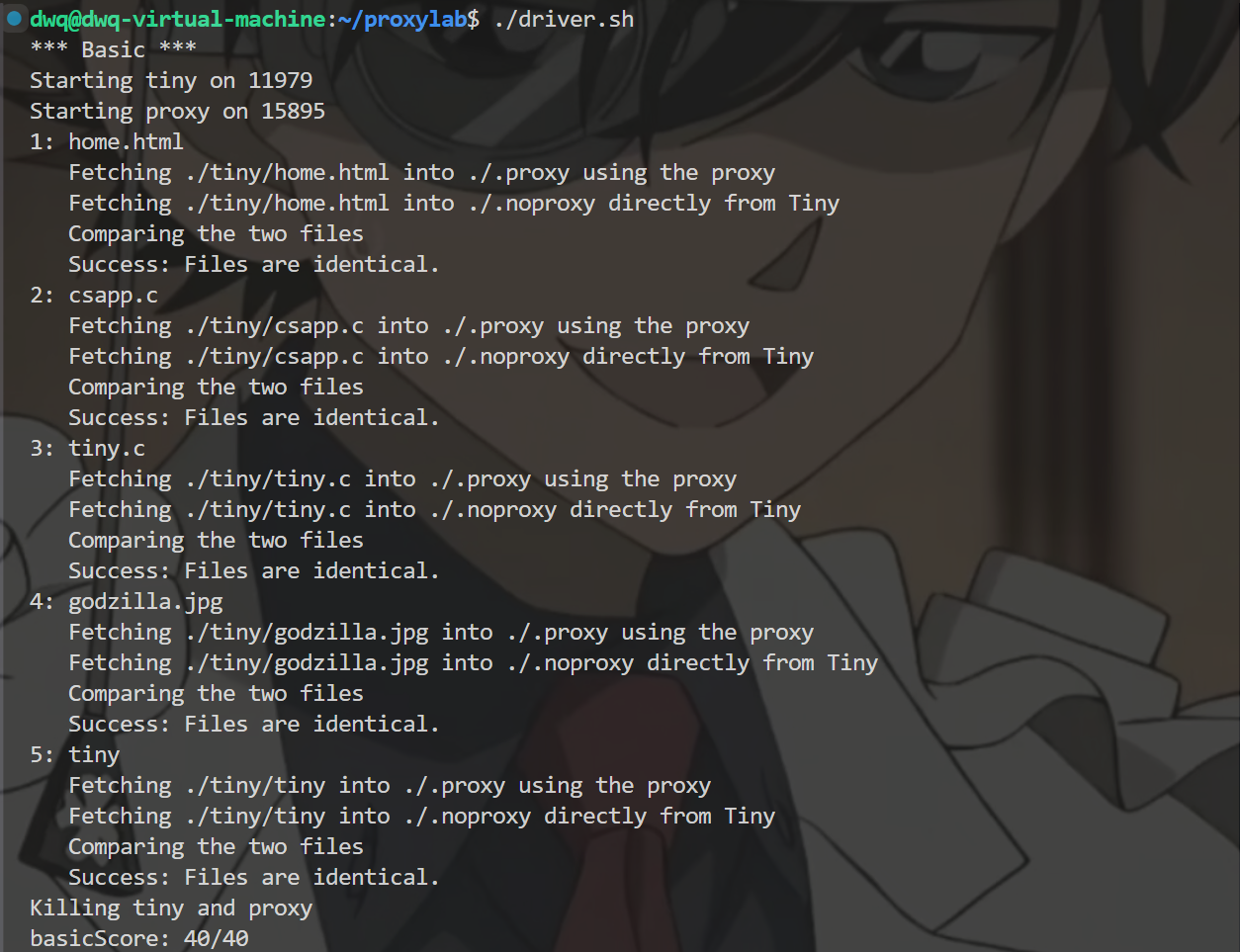
最后的totalScore为40/70
2. 处理多个并发请求
概述
- 采用多线程方式实现服务器并发:
- 主线程负责监听端口
- 每有一个客户端连接时,分配一个新线程单独为这个客户端提供服务
- 实现:main死循环监听端口,每当有一个连接进入时,创建并分配一个新线程进行服务,服务结束后这个线程回收
- 为了减少线程创建销毁的效率,采用预线程化:
- 服务器初始化时就创建一定数量的线程(处于挂起的状态)
- 主线程监听端口,当有连接进入时,激活一个挂起的线程进行服务
- 服务完成后,线程接着挂起
- 如果连接进来时所有线程都忙碌,则将连接的描述符插入缓冲区中
代码实现
- 添加新的库
1 |
- 定义新常量
1 | // 并发相关常量 |
- 在main函数中添加多线程处理的相关函数(生产者-消费者模型)
1 | pthread_t tid; // 线程标识符变量 |
- 增加线程工作函数
1 | void *thread(void *vargp){ |
- SBUF(共享缓存区)结构和函数的实现
1 | void sbuf_init(sbuf_t *sp, int n){ |
检测
1 | make clean |
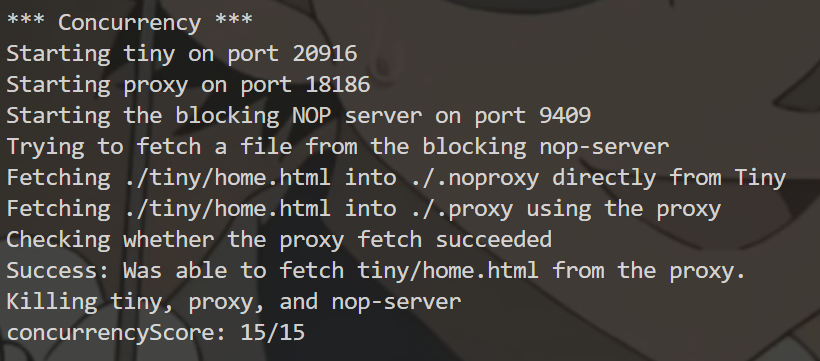
最后totalScore: 55/70
3. 缓存Web对象
概述
- 为所实现的代理添加一个缓存,用于将最近使用的Web对象存储在内存中,缓存需要实现LRU替换策略
- 由于读操作频率远大于写操作频率,此处使用读者-写者模型(并发模型):
- 读者之间不互斥(默认读者不进行写操作),可以让多个读者对同一个缓存读操作
- 写者互斥,不仅和其他写者互斥,和读者也互斥
- 优先安排读操作
- 需要实现缓存结构以及相关函数
代码实现
- 创建cache.h,实现相关结构
1 |
|
- 创建cache.c,实现相关函数
1 |
|
- 添加cache.h (后续函数更改在proxy.c中实现)
1 |
- 增删相关定义
1 | // 此处在cache.h定义了,所以注释掉 |
- 在doit()中添加相关参数
1 | void doit(int fd, Cache *cache); |
- 在doit()中添加cache相关代码
1 | char complete_uri[MAXLINE] = ""; // 存储完整的URI |
- 在thread()函数中修改doit()中的参数
1 | doit(connfd, global_cache); |
- 修改Makefile (增加对cache.c cache.h的编译)
1 | # 增加 |
检测
1 | make clean |
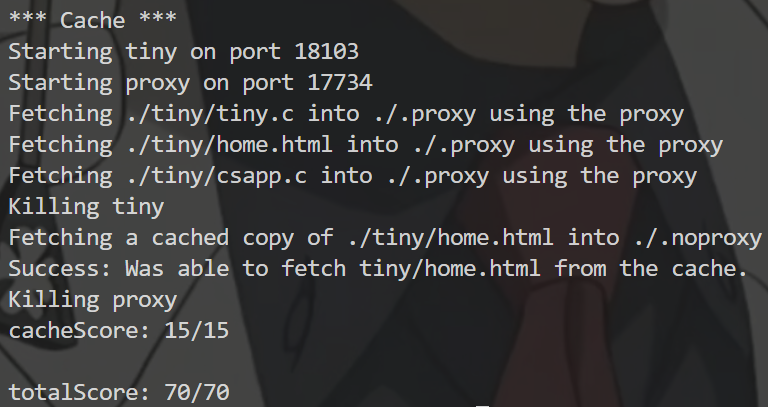
最后totalScore: 70/70
提交
1 | make handin |
在父目录中生成handin.zip
proxy结束!✿✿ヽ(°▽°)ノ✿完结撒花!
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 QingMaxLim-Blog!