NEMU_PA3
阶段一
第一次没过破防了决定直接一部到胃一起写必做一和选做一
1. 概述
- 根据指导书可知,我们需要实现一级高速缓存和二级告诉缓存,其中l2会多一个脏标签的处理
- 公式:C=B* E *S (E缓存块 B字节 S组 C总大小)
- l1: E=8 B=64 C=64*1024 S=128
- l2: E=8 B=64 C=4*1024 *1024 S=4096
- Address:
- tag: t bits
- set index: s bits
- block offset: b bits
- l1: b=6 s=7
- l2: b=6 s=12
2. 实现
- 定义高速缓存的结构(nemu/include/memory/cache.h)
1 |
|
- 实现相关函数(nemu/src/memory/cache.c)
1 | //初始化高速缓存 |
- 更改hwaddr_read()和hwaddr_write() (nemu/src/memory/memory.c)
1 | uint32_t hwaddr_read(hwaddr_t addr, size_t len) { |
- 由于被多次调用的读写操作函数位于dram.c文件中的,其中有两个函数是用static封装,则需在dram.c文件中进行全局变量的声明(作为接口调用这两个函数)
1 | void ddr3_read_me(hwaddr_t addr, void* data) { |
3. 调试
1 | make clean |
通过即可
阶段二
模拟IA-32的分段机制
- 修改kernel/include/common.h:去掉**#define IA32_SEG*的注释
- 根据报错信息和指导手册,现在需要补全lgdt指令(修改nemu/include/cpu/reg.h)
- 段寄存器索引枚举
1 | enum { R_CS, R_DS, R_SS, R_ES }; |
- 定义段寄存器结构
1 | // CR0 CR3定义在libcommon/x86-inc/cpu.h中,添加头文件 |
- GDT描述符读取结构
1 | typedef struct { |
- 定义分段机制相关寄存器
1 | union { // 段寄存器 |
- 在restart()函数中初始化分段机制相关的寄存器(修改nemu/src/monitor/monitor.c)
1 | /* 初始化CR0寄存器 - 实模式 */ |
- 创建 nemu/src/cpu/exec/data-mov/lgdt.h
1 |
|
- 创建 nemu/src/cpu/exec/data-mov/lgdt.c
1 |
|
- 创建 nemu/src/cpu/exec/data-mov/lgdt-template.h
1 |
|
- 在nemu/src/cpu/exec/exec.c中修改group7的定义
1 | make_group(group7, |
- 在nemu/src/cpu/exec/all-instr.h中添加声明
1 |
- 实现操作CR0和CR3的mov指令,修改nemu/src/cpu/exec/data-mov/mov-template.h:
1 |
|
- 在nemu/src/cpu/exec/data-mov/mov.h中添加声明:
1 | make_helper(mov_cr2r); |
- 在nemu/src/cpu/exec/exec.c的*_2byte_opcode_table*中注册指令:
1 | /* 0x20 */ mov_cr2r, inv, mov_r2cr, inv, |
- 修改nemu/include/memory/memory.h
1 | uint32_t swaddr_read(swaddr_t, size_t, uint8_t); |
- 修改nemu/include/cpu/exec/template-start.h中的MEM宏
1 |
- 在nemu/src/memory/memory.c中实现seg_translate函数并修改修改swaddr_read和swaddr_write函数(虚拟地址->线性地址)
1 | // 添加 |
- 修改nemu/include/cpu/decode/operand.h
1 | typedef struct { |
- 修改nemu/src/cpu/decode/modrm.c(在read_ModR_M函数中设置rm->sreg)
1 | // read_ModR_M()修改部分 |
在load_addr()中:
1 | rm->reg = m->R_M; |
- 之后需要修改所有涉及到swaddr函数的参数和MEM宏定义的参数,排查方式:
1 | grep -r "swaddr_read" nemu/src/ --include="*.c" -n |
经过排查之后,修改如下:
1 | // nemu/src/cpu/exec/data-mov/leave.c |
- 实现段寄存器mov:nemu/src/cpu/exec/data-mov/mov-template.h中添加:
1 |
|
在mov.h添加声明
1 | make_helper(mov_sreg2rm); |
- 在nemu/src/cpu/reg.c中的更新描述符cache
1 | void sreg_set(uint8_t id) { // 根据段描述符 更新 段描述符高速缓存 |
- 在nemu/include/cpu/reg.h中添加声明
1 | void sreg_set(uint8_t id); |
- 在nemu/src/cpu/exec/exec.c中注册
1 | /* 0x8c */ inv, lea, mov_sreg2rm, inv, |
- 在nemu/src/monitor/monitor.c中添加调用
1 | static void init_cs() { |
- 在nemu/src/cpu/exec/control/jmp-template.h中添加ljmp指令
1 | make_helper(ljmp) { |
在jmp.h中声明
1 | make_helper(ljmp); |
- 在nemu/src/cpu/exec/exec.c的opcode_table中注册
1 | /* 0xe8 */ call_i_v, jmp_si_l, ljmp, jmp_si_b, |
- 进行检测
1 | sudo docker start nemu-image |
结果如下: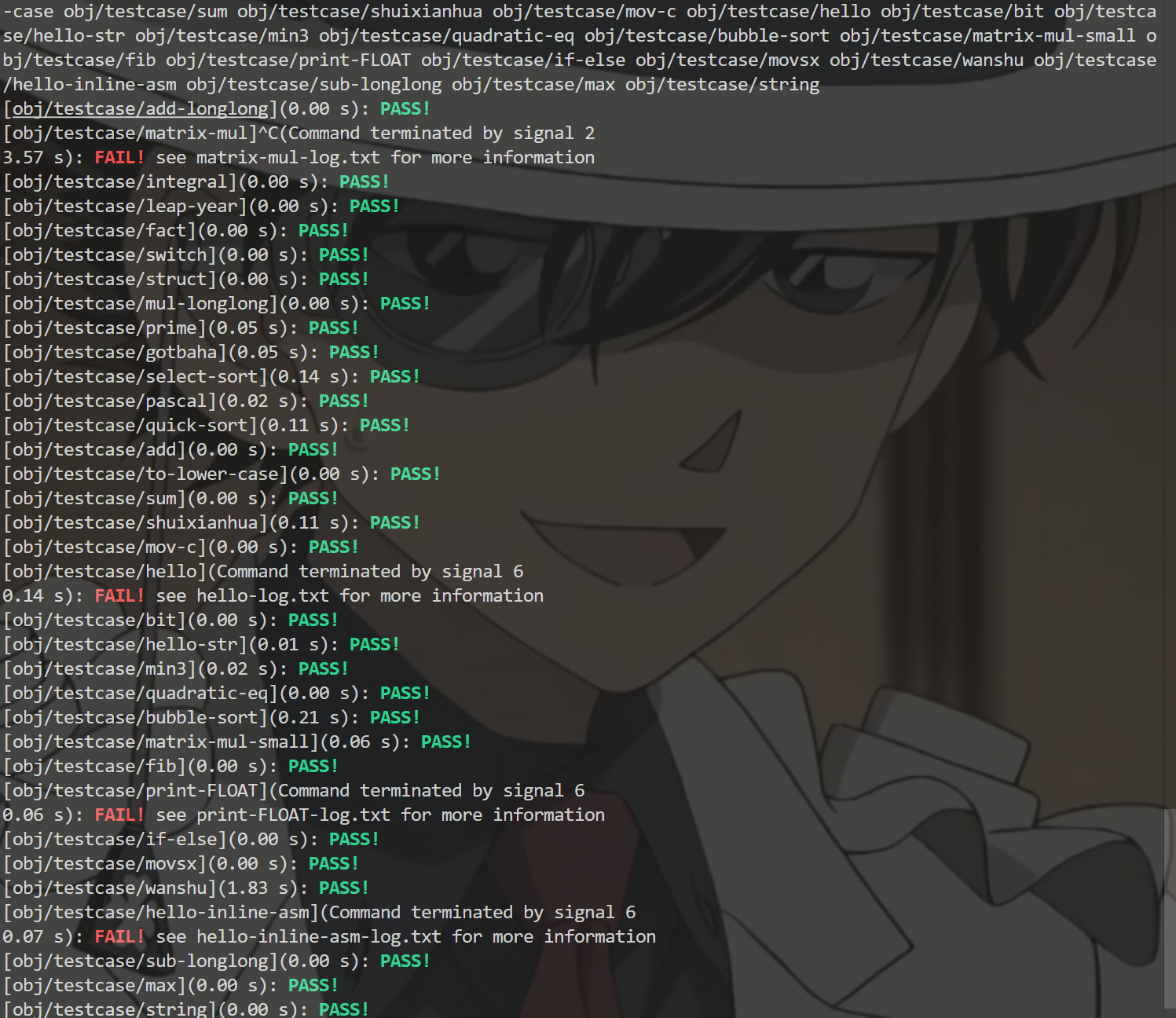
阶段三
在阶段二的基础上实现分页机制,这次还是必做选做一起搞了
- 添加CR3寄存器(阶段二已经完成了)
- 为CR0寄存器添加PG位的功能。装载CR0后, 如果发现CR0的PE位和PG位均为1, 则开启 IA-32 分页机制, 从此所有线性地址的访问(包括 lnaddr_read(), lnaddr_write())都需要经过页级地址转换。在 restart()函数中对CR0寄存器进行初始化时, PG位要被置0(阶段二已经完成了)
- 修改kernel/include/common.h:去掉**#define IA32_PAGE的注释,修改kernel/Makefile.part*中的链接选项,使用虚拟地址,通过页表映射到物理地址0x00100000
1 | kernel_LDFLAGS := -m elf_i386 -e start -Ttext=0xc0100000 |
- 修改nemu/src/memory/memory.c中的lnaddr_read(),lnaddr_write()函数实现页级地址转换
1 | // 添加头文件 |
- 实现cld指令
1 | // 创建nemu/src/cpu/exec/string/cld.h |
- 实现std指令
1 | // 创建nemu/src/cpu/exec/string/std.h |
注册(nemu/src/cpu/exec/exec.c)
1 | /* 0xfc */ cld, std, group4, group5, |
声明(nemu/src/cpu/exec/all-instr.h)
1 |
- 为用户进程分配虚拟空间,修改kernel/src/elf/elf.c
1 | // 添加头文件 |
- 在nemu/src/memory/memory.c中实现用于调试的页表转换函数
1 | hwaddr_t cmd_page(lnaddr_t addr) { |
在nemu/include/memory/memory.h中添加声明
1 | hwaddr_t cmd_page(lnaddr_t addr); |
修改nemu/src/monitor/debug/ui.c
1 |
|
- 实现tlb:创建nemu/include/memory/tlb.h
1 |
|
创建nemu/src/memory/tlb.c
1 |
|
修改nemu/src/monitor/monitor.c
1 | // 添加 |
- 实现create_video_mapping()函数来为用户进程创建显存的恒等映射(kernel/src/memory/vmem.c)
1 | // 在void create_video_mapping()添加 |
- 更改nemu/src/cpu/exec/exec.c的opcode
1 | /* 0x2c */ inv, sub_i2a_v, inv, inv, |
- 增添sub_i2a()函数
nemu/src/cpu/exec/arith/sub-template.h
1 | make_instr_helper(i2a) |
nemu/src/cpu/exec/arith/sub.c
1 |
|
nemu/src/cpu/exec/arith/sub.h
1 | make_helper(sub_i2a_v); |
- 增添push_i_v()
nemu/src/cpu/exec/arith/push-template.h
1 | // 更改do_execute() |
nemu/src/cpu/exec/arith/push.c
1 | make_helper_v(push_i) |
nemu/src/cpu/exec/arith/push.h
1 | make_helper(push_i_v); |
- 注册jg_l(),更改nemu/src/cpu/exec/exec.c的opcode
1 | /* 0x8c */ inv, jge_l, jle_l, jg_l, |
- 进行检测
1 | make clean |
结果如图: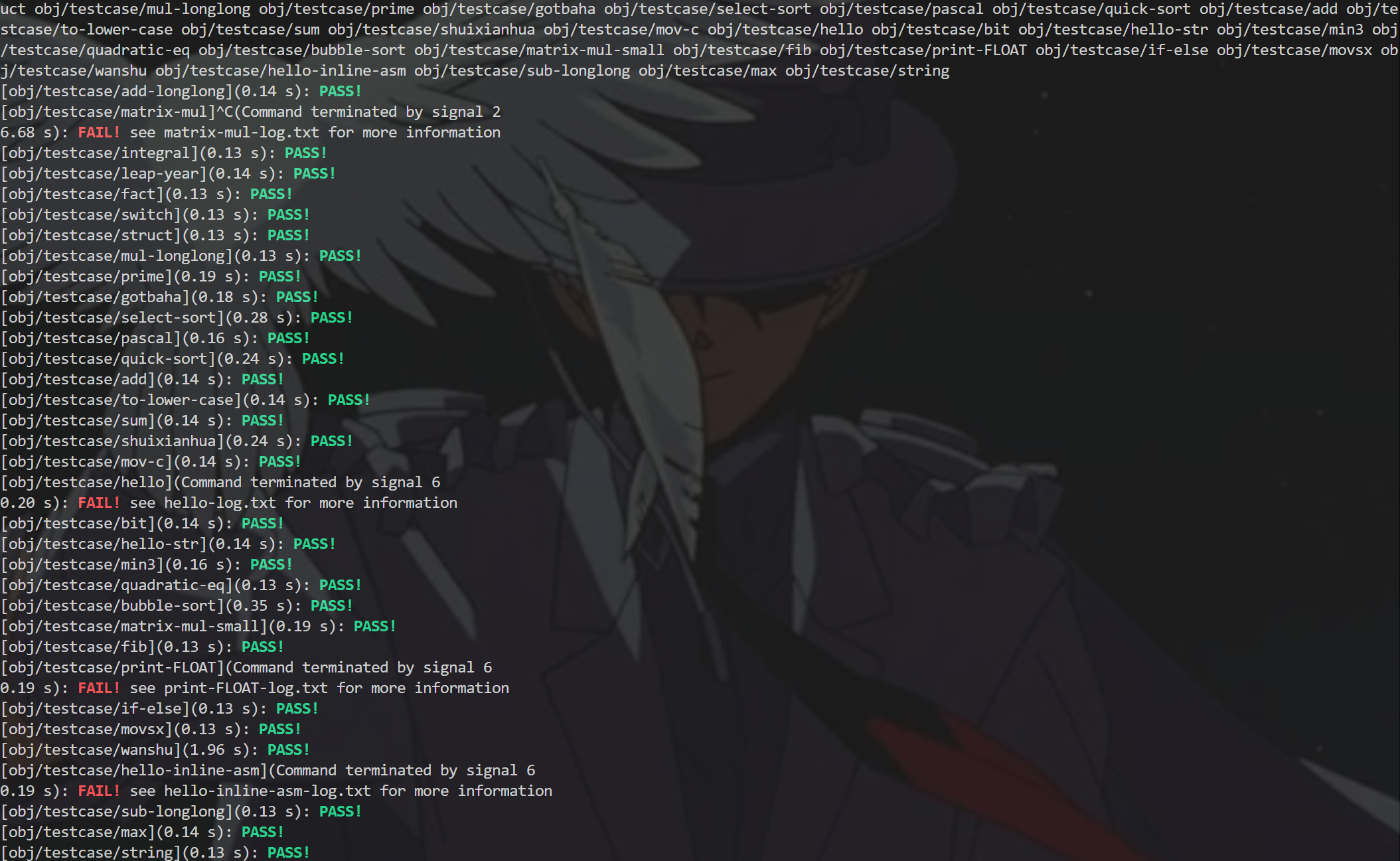
16. 提交(别翻指导书了这里直接告诉你哈哈啊哈哈)
1 | make submit |
NEMU_PA3经6次秽土重生后结束!✿✿ヽ(°▽°)ノ✿完结撒花!
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来源 QingMaxLim-Blog!